LoRa and LoRaWAN Technology Detailed Explanation and Application Solutions
1. What is LoRa?
LoRa (Long Range) is a wireless communication technology known for its long transmission distance, low power consumption and strong anti-interference ability. It is particularly suitable for scenarios that require long-term operation and large-scale coverage, such as smart cities and environmental monitoring.
(1) Comparison with other wireless communication technologies
Compared with technologies such as 4G, WiFi, NB (Narrowband Internet of Things) and Bluetooth, LoRa has lower data transmission rate and capacity, but its advantages are:
- Longer transmission distance: Wider coverage than WiFi.
- Lower power consumption: Suitable for long-term battery-powered applications.
- Lower cost: No need to pay for data traffic like 4G.
(2) LoRa networking mode
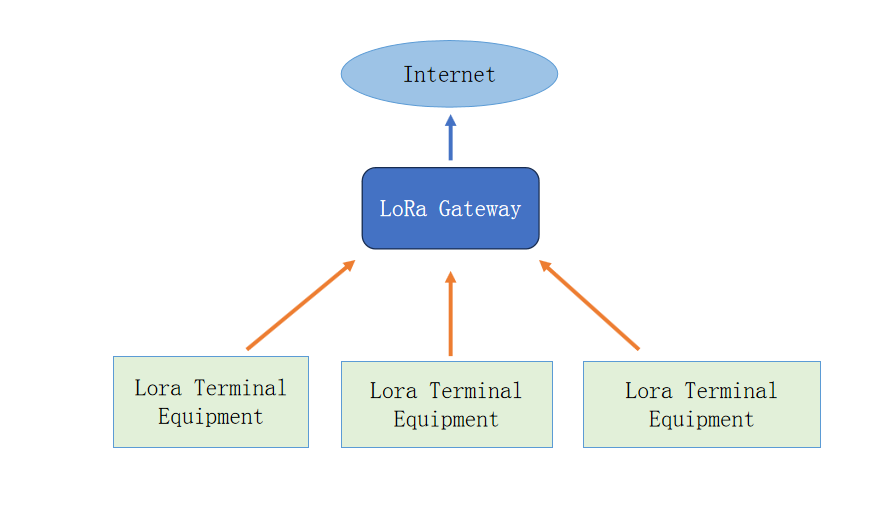
LoRa supports point-to-point communication and star networking, and realizes centralized collection and forwarding of data from multiple nodes through gateway devices.
2. What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a protocol layer specification developed based on the LoRa physical layer technology. It defines the data transmission format and utilizes AES encryption technology, significantly improving data standardization and security. The LoRaWAN standard is managed by the LoRa Alliance and recognized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) as the global standard for low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs).
3. Characteristics and applications of LoRaWAN
Characteristics:
- Long distance communication
- Low power consumption
- Strong anti-interference capability
- Low cost
Each country and region has its own legal frequency band specifications. Common ones are: CN470 (Chinese standard), EU868 (European standard), AU915 (Australian standard), US915 (US standard), AS923 (other Asian country standards)
Application areas:
- Smart meters (such as electricity meters, water meters)
- Smart cities and smart buildings
- Intelligent public transportation
- Manufacturing Internet of Things
- Logistics and personnel tracking
- Environmental sensing and smart agriculture
(1) LoRaWAN networking mode
LoRaWAN adopts a star topology. Terminal devices send data to the network server through the gateway, and then forward it to the application platform.
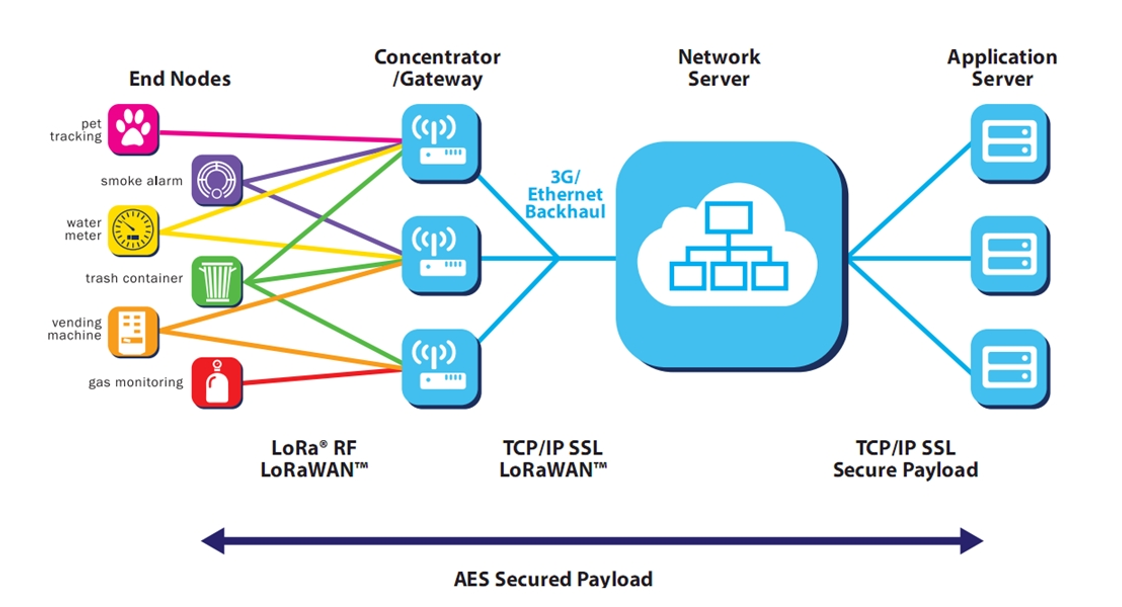
(2) Comparison between LoRaWAN devices and WiFi and 4G devices
| LoRaWAN | WiFi | 4G | |
| Networking | LoRaWAN gateway | Router | Base stations |
| Transmission distance comparison | Longer | Short | Generally longer distances |
| Transmission rate comparison | Slower | Fast | Fast |
| Power consumption | Low | High | High |
| Data capacity | Amount | Large | High volume |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High (also consider data charges) |
4. LoRaWAN electricity meter
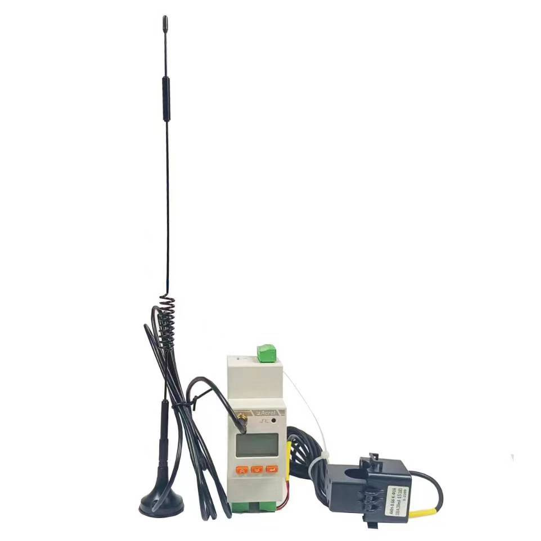
(1) Single-phase wireless meter: ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868
Suitable for single-phase electricity metering, supports LoRaWAN communication, and can realize remote data collection and monitoring.

(2) Three-phase wireless meter: ADW300-LW series
Designed for three-phase power systems, it has high-precision metering and remote communication functions and is suitable for industrial and commercial scenarios.

5. LoRaWAN Data Conversion Module
(1) AWT100-LW Series
This module communicates with terminal devices that do not support LoRaWAN via the RS485 interface using the Modbus protocol. After collecting data, it sends it to the gateway via LoRaWAN, enabling IoT upgrades for traditional devices.

(2) LoRaWAN Gateway: AWT200-LW Series
The gateway is responsible for receiving LoRaWAN signals sent by terminal devices and forwarding data to the server via Ethernet. It is the core device of the LoRaWAN network.

6. LoRaWAN Gateway Networking Solution
(1) Third-party Gateway Solution
- Terminal Device: LoRaWAN Meter or Data Conversion Module
- Uplink Gateway: Third-party LoRaWAN Gateway (such as Milesight)
- Platform: User’s third-party platform or own platform
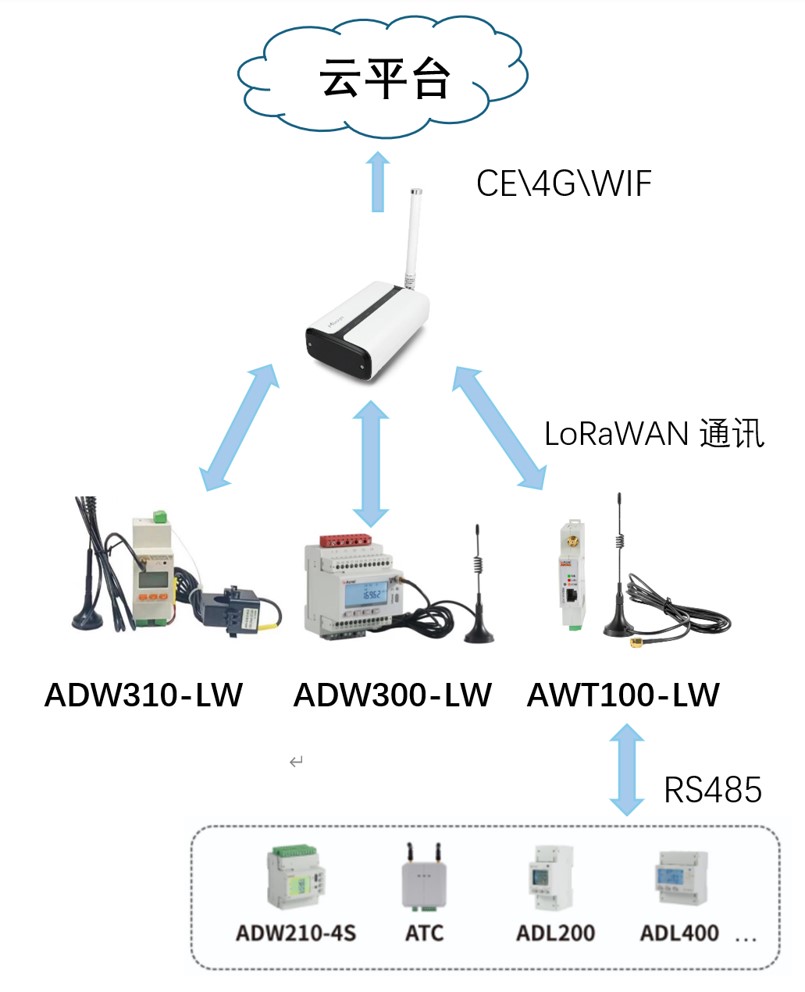
(2) Own Gateway Solution
- Gateway: AWT200-LW923
- Terminal Device: LoRaWAN Meter or Data Conversion Module
- Platform: Own Platform
- Note: It is not recommended to connect to a third-party platform to ensure system compatibility and stability.

7. LoRaWAN Device Model-Frequency Band Comparison Table
| ADW300-LW | ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868 | AWT100-LW | AWT200-LW | ||
| China | CN470 | ADW300-LW470 | AWT100-LW470 | AWT200-LW470 | |
| Part of Europe | EU868 | ADW300-LW868 | ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868 | AWT100-LWHW | AWT200-LW868 |
| Australia | AU915 | ADW300-LW915 | ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868 | ||
| North America | US915 | ADW300-LW915US | ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868 | ||
| Asia (excluding Japan and South Korea) | AS923 | ADW300-LW923 | ADW310-HJ-D16/LW868 | AWT200-LW923 |
-
The "Stethoscope" of Power Systems: Why You Need a Power Quality Analyzer
 Part 1: Introduction 1.1 What is Power Quality and Why is it Important? In modern society, a stable ...View More
Part 1: Introduction 1.1 What is Power Quality and Why is it Important? In modern society, a stable ...View More -
Advancements and Applications of AC Energy Meters in Modern Power Management
 Introduction to AC Energy Meters In today’s rapidly evolving energy sector, accurate measurement and...View More
Introduction to AC Energy Meters In today’s rapidly evolving energy sector, accurate measurement and...View More -
What are the key differences between a basic thermal overload relay and a smart motor protection relay?
 I. Introduction: The Critical Need for Motor Protection Electric motors are the undisputed workhorse...View More
I. Introduction: The Critical Need for Motor Protection Electric motors are the undisputed workhorse...View More -
Precision and Versatility: Unlocking Efficiency with Panel Mount Multifunction Meters
 Introduction In modern industrial and commercial power environments, precise measurement and managem...View More
Introduction In modern industrial and commercial power environments, precise measurement and managem...View More
 Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected] Phone: +86-18702106858 / +86-21-69156352
Phone: +86-18702106858 / +86-21-69156352


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch